-
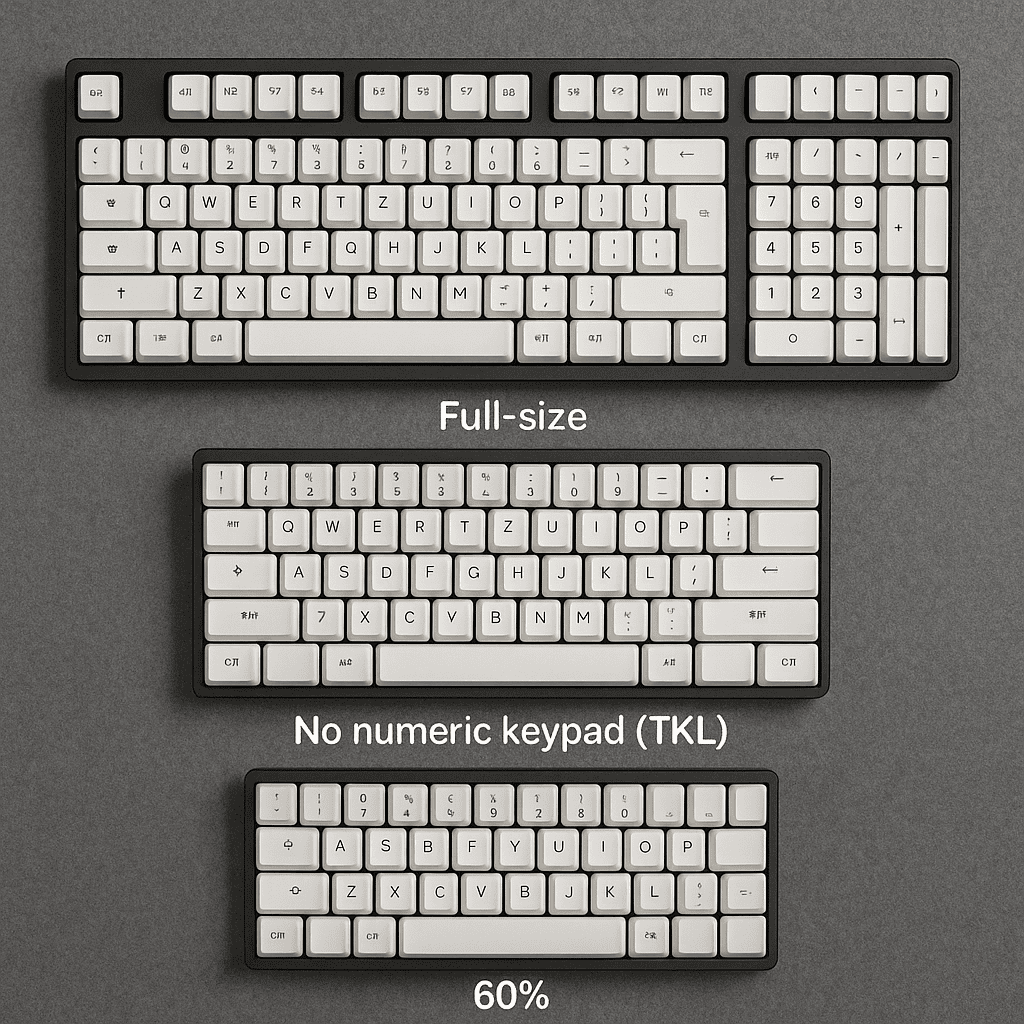

Size Matters: 60% vs. TKL vs. Full-Size – Which Keyboard Layout is Right for You?
•
Introduction When you decide to buy a new mechanical keyboard, you’re often met with a barrage of confusing…
-
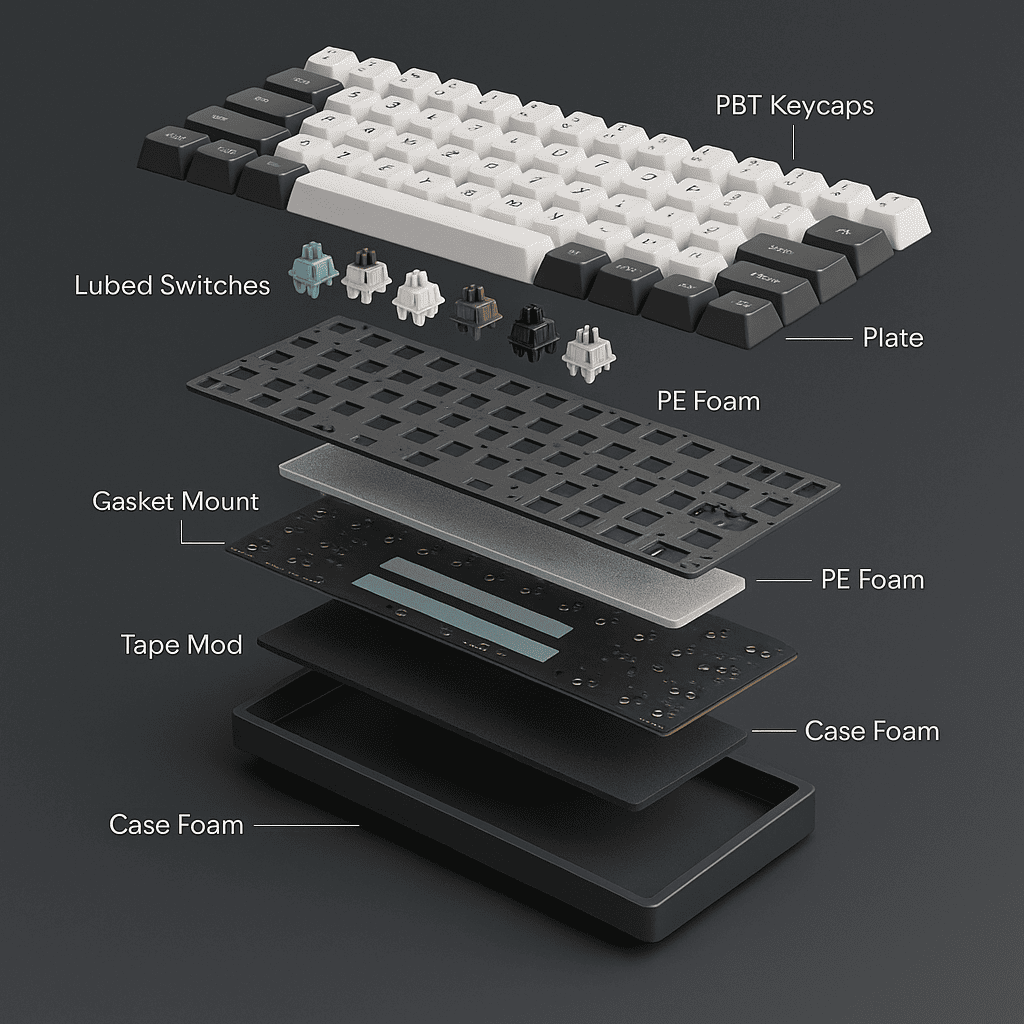
Beyond the Click: The Ultimate Guide to Tuning Your Keyboard’s Sound
•
Introduction Close your eyes and listen. In the soundscape of the modern workspace, you can often hear the…
-
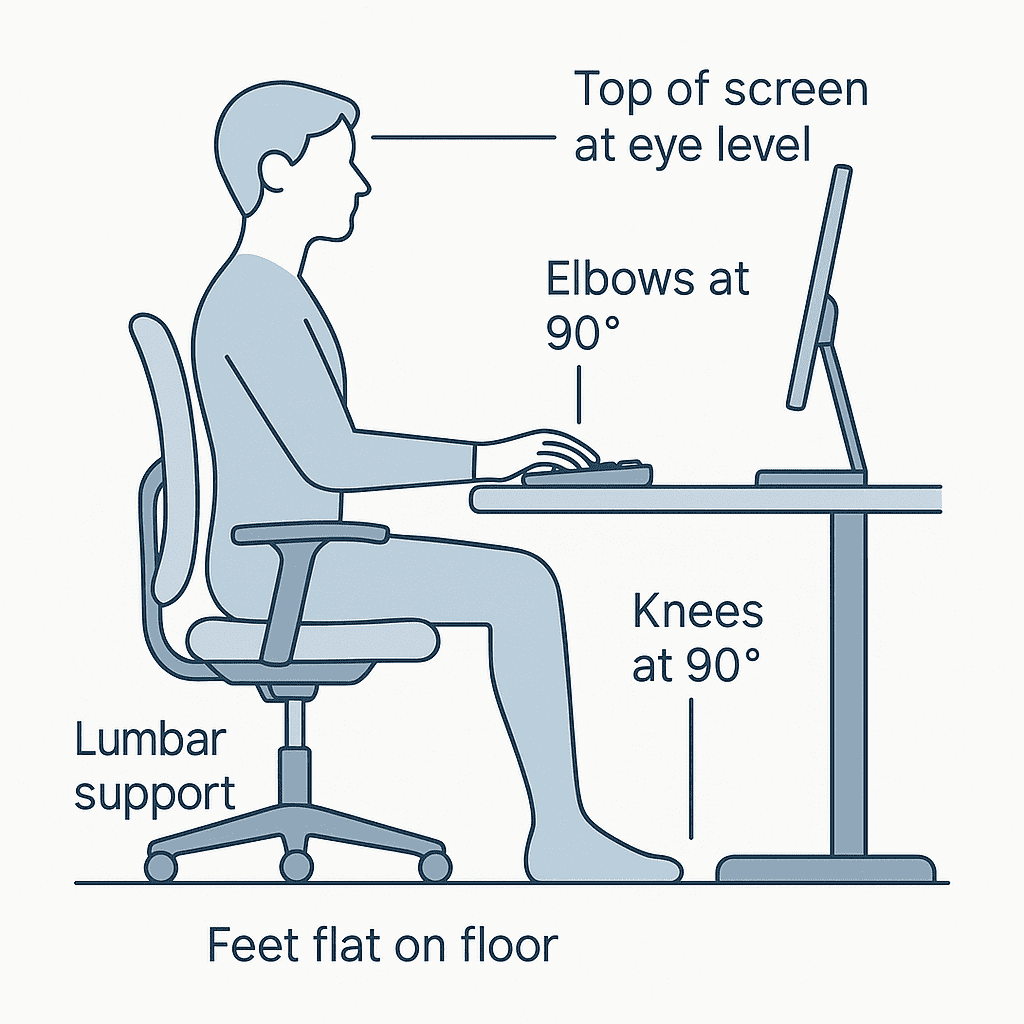
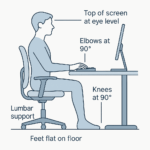
Beyond the Keyboard: A Step-by-Step Guide to the Perfect Ergonomic Workspace
•
Introduction You’ve finished a long day of work, and as you stand up, you feel it: the dull…
-

From Novice to Ninja: A Comprehensive Guide to Mastering Keyboard Shortcuts for Productivity
•
Introduction Take a moment to think about your typical workday. How many times do your hands leave the…
-

The Best Ergonomic Keyboards in 2025: A Guide to Comfort and Productivity
•
Introduction In our increasingly digital world, the hours we spend typing can take a toll on our bodies.…
-

The Ultimate Guide to Keyboard Maintenance and Customization
•
Introduction Have you ever stopped to think about your keyboard? It’s one of the most used peripherals in…
-

Unlocking Comfort: A Comprehensive Guide to Ergonomic Keyboard Setup
•
Introduction Tired of wrist pain, shoulder aches, or just general discomfort after a long day at your keyboard?…
-

10 Productivity Tips to Maximize Your Mechanical Keyboard in a Work-from-Home Setup
•
Boost your work-from-home efficiency with these 10 mechanical keyboard productivity tips, including shortcuts, custom layouts, and ergonomic setups.
Search
Recent Posts
- Size Matters: 60% vs. TKL vs. Full-Size – Which Keyboard Layout is Right for You?
- Beyond the Click: The Ultimate Guide to Tuning Your Keyboard’s Sound
- Beyond the Keyboard: A Step-by-Step Guide to the Perfect Ergonomic Workspace
- From Novice to Ninja: A Comprehensive Guide to Mastering Keyboard Shortcuts for Productivity
- The Best Ergonomic Keyboards in 2025: A Guide to Comfort and Productivity