generative-ai-future-of-work
•
•
Search
Recent Posts
- Beyond the Click: The Ultimate Guide to Tuning Your Keyboard’s Sound
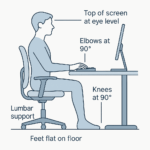
- Beyond the Keyboard: A Step-by-Step Guide to the Perfect Ergonomic Workspace
- From Novice to Ninja: A Comprehensive Guide to Mastering Keyboard Shortcuts for Productivity
- The Best Ergonomic Keyboards in 2025: A Guide to Comfort and Productivity
- The Ultimate Guide to Keyboard Maintenance and Customization